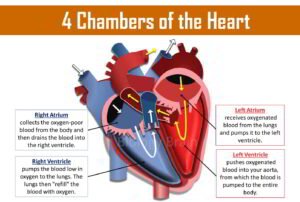
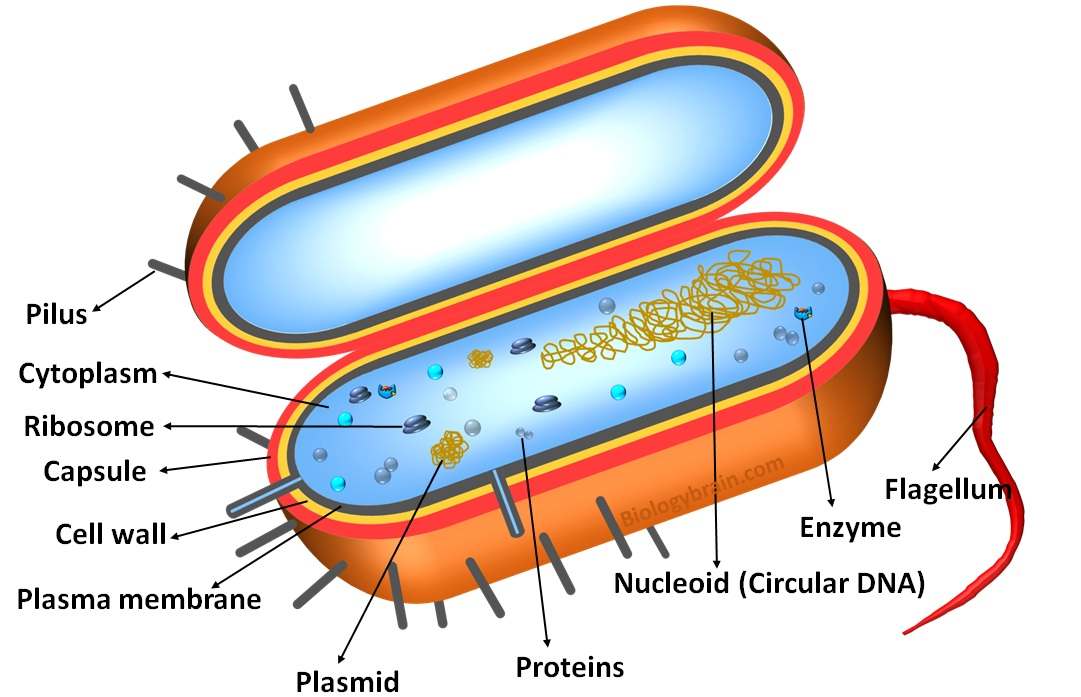
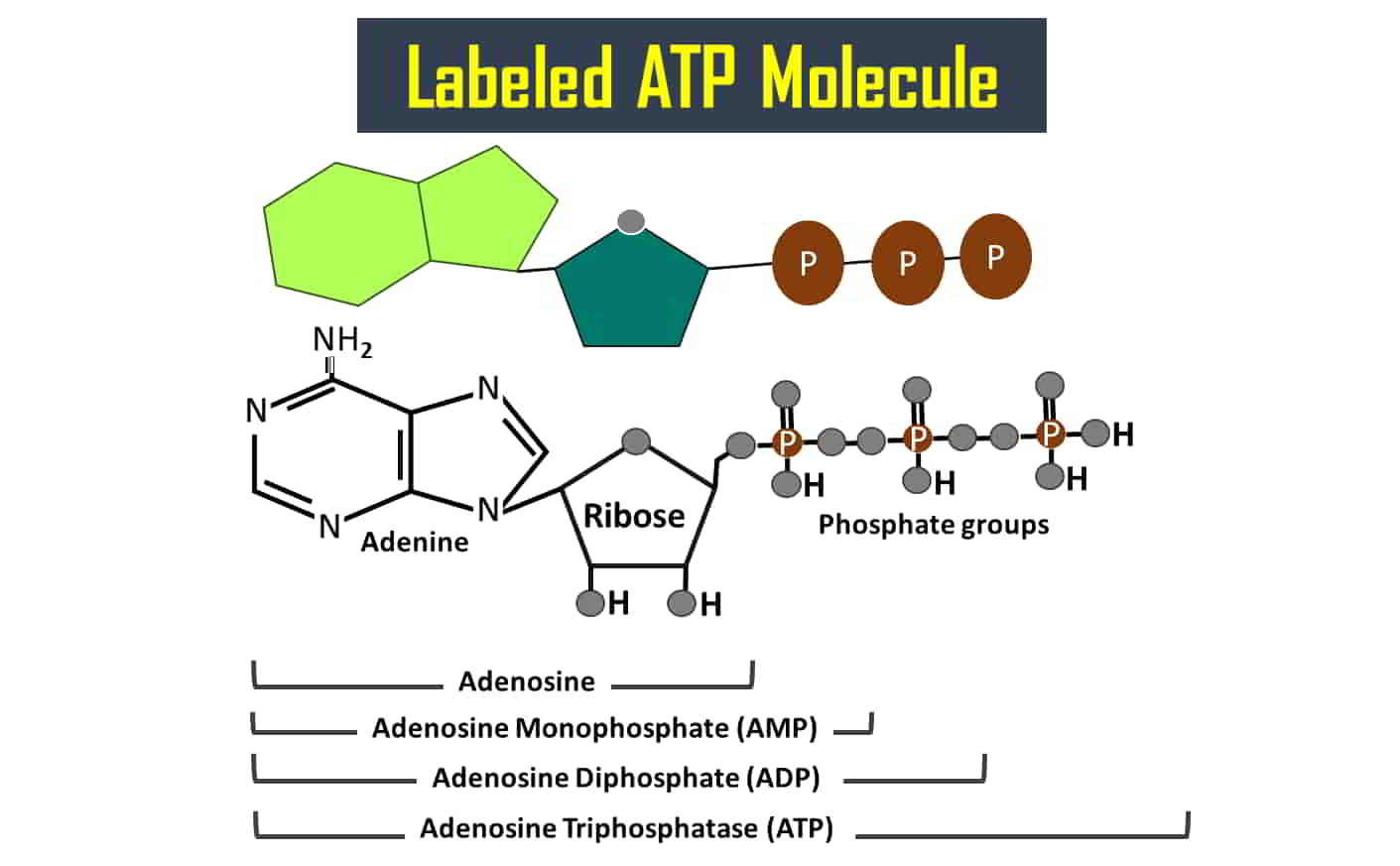
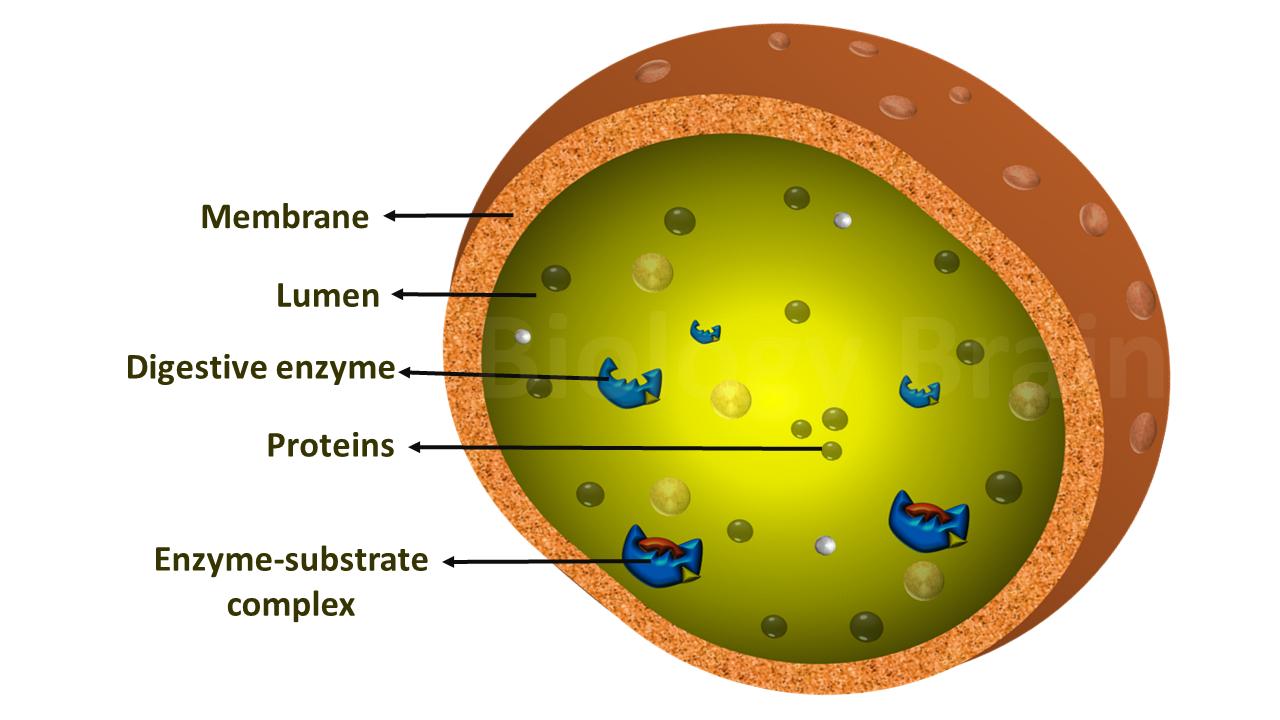
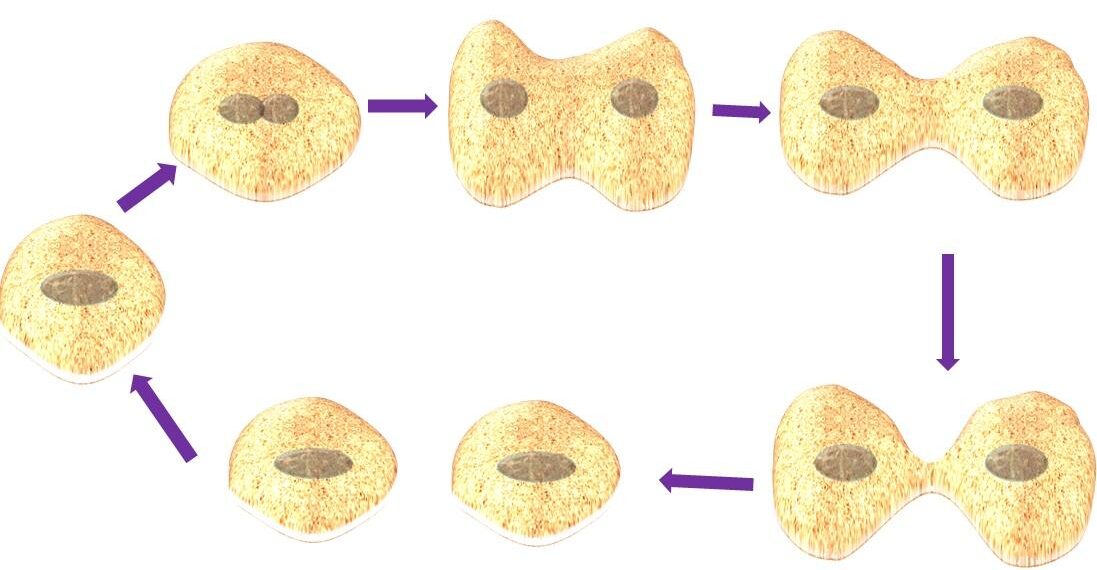
The three kingdom classification was given by the German scientist, Haeckel Ernst, in the 1860s. He divided the organisms into three kingdoms, such as Animalia, Plantae, and Protista.
He arranged organisms based on complexities in morphological and tissue systems, division of labor, and mode of nutrition.
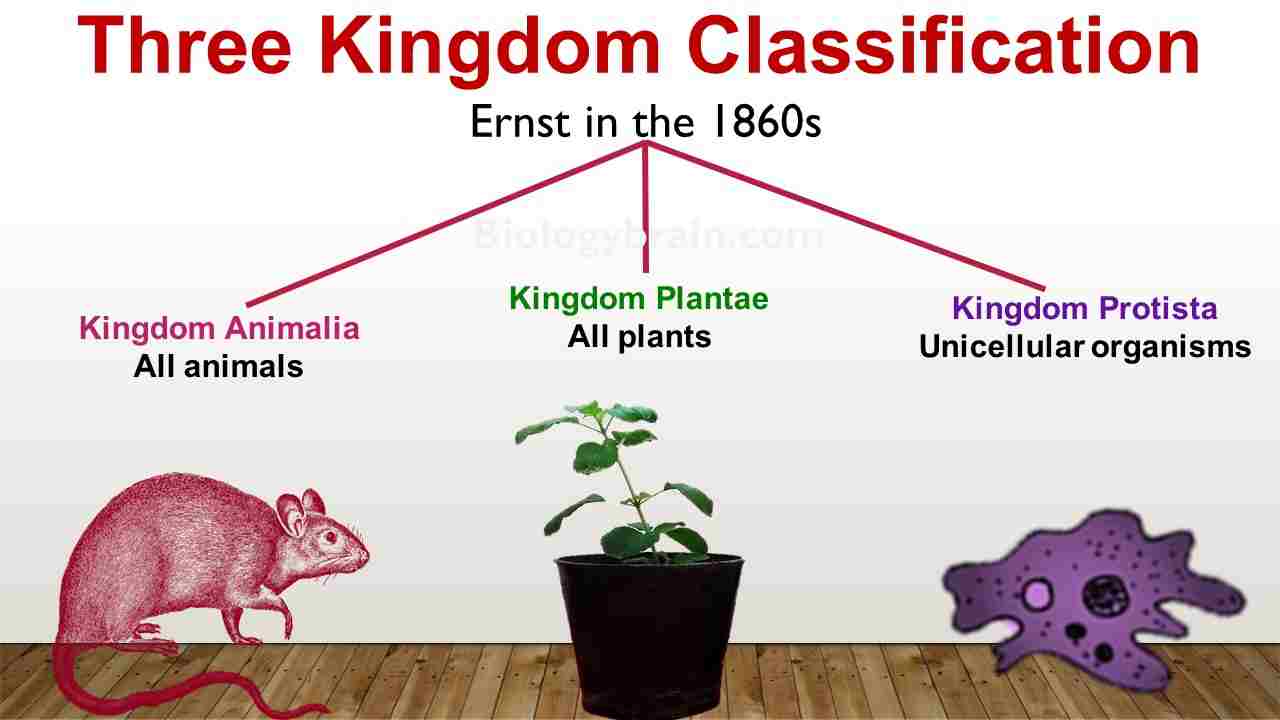
Kingdom Protista
The organisms without morphological complexities, moderate tissue systems, and division of labor, and those performing various types of modes of nutrition, were separated and placed under the kingdom Protista. Under the kingdom of Protista, he placed protozoa, algae, fungi, and bacteria.
Kingdom Plantae
Organisms that possess morphological complexities and well-defined division of labor, diverse tissue system, and autotrophic mode of nutrition, were placed under kingdom Plantae.
Kingdom Animalia
Organisms that possess maximum morphological complexities and well-defined division of labor with diverse tissue-system, and holophagic (phagotrophic) modes of nutrition, were placed under kingdom Animalia. However, this three-kingdom system was not widely accepted.
Other Biology Topics
| Cell organelles | Lysosome function |
| Mitochondria function | Lysosomal enzymes |
| Diagram of Lysosome | Lysosomal storage diseases |