Herbivore Definition: Herbivores are animals that only eat plant-based materials, such as leaves, fruits, stems, seeds, nectar, roots, bark, etc.
The term “herbivore” refers to animals that chew leaves, and insects that harm a plant by sucking sap, as well as more benign species that only gather pollen, nectar, or plant resin.
Both terms have Greek roots: “phyton,” which means “plant,” and “phagein,” which means “to eat or devour.”
There are thousands of herbivorous animals in the ecosystem.

Herbivores Animals Name-List | |
Animal | Its Feed |
| Antelope | Bushes, smaller trees, and grass. |
| Beaver | Leaves, twigs, shrubs, ferns, aquatic plants, grasses, crops, etc. |
| Bison | Grasses, weeds, and leafy plants. |
| Buffalo | Grasses, rice straw, weeds, and leafy plants. |
| Camel | Grass, grains, and wheat. |
| Cow | Grasses, rice straw, weeds, and leafy plants. |
| Deer | Leaves, twigs, shoots of plants, vines, and rarely grass. |
| Donkey | Barley straw, hay, and grass. |
| Iguanas | Leaves from trees and vines. |
| Bees | Pollen and nectar. |
| Earthworms | Decaying roots and leaves. |
| Rhinoceroses | Grass, twigs, leaves, and small branches. |
| Rabbits | Hay, grass, fresh vegetables, few pellets |
| Goat | Weeds, grasses, hay, grains, and small tree barks. |
| Oxe | Grasses, rice straw, weeds, and leafy plants. |
| Few Birds (sugarbirds, Cassowaries, Canada Geese, etc) | Fruits, seeds, etc. |
| Herbivorous Fish (Acanthurus Lineatus, Acanthurus Nigrofuscus, Parrotfish, and Unicornfishes). | Algae and leaves of small plants. |
However, the herbivores have been separated into several groups based on their feeding strategies.
Animal | Its Feed | Examples |
| Algivores | Algae | Herbivorous fish |
| Detritovore | Decaying plant materials | Few earthworms, etc. |
| Frugivores | Fruit | Orangutans, hammer-headed bats, gorilla, etc. |
| Folivores | Leaves | Iguanas, koalas, etc. |
| Nectarivores | Nectar | Bees, sugarbirds, etc. |
| Granivores | Seeds | Finches, sparrows, etc. |
| Palynivores | Pollen | Many insects and some mites etc. |
| Mucivores | Plant fluids, mainly sap | Some insects and birds. |
| Xylophages | Wood | Beavers, gribbles, wood-boring beetles, etc. |
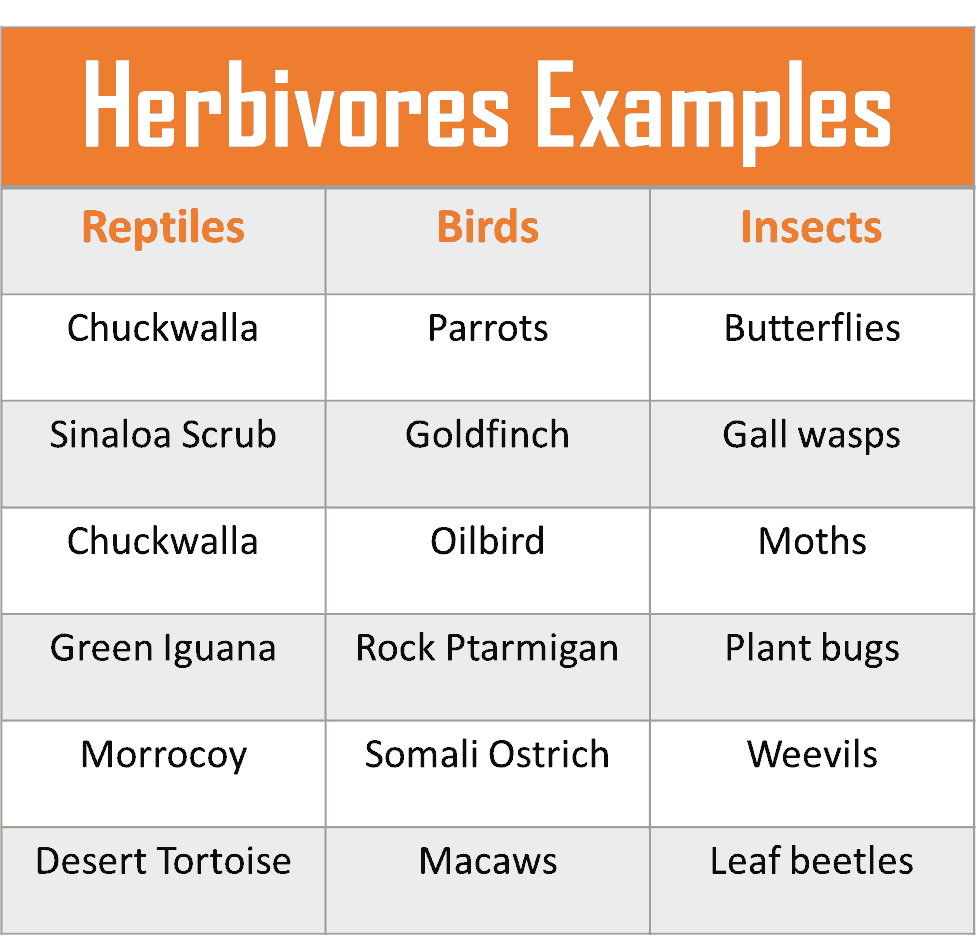
21 Examples of Herbivorous Birds
- Common Ostrich
- Evening Grosbeak
- Hoatzin
- House Finch
- Hummingbirds
- Parrots
- Oriole
- Goldfinch
- Gray Geese
- Macaws
- Canada Geese
- Pine Siskin
- Red Finches
- Large Waterfowl
- Nene
- Oilbird
- Somali Ostrich
- Sulphur-Crested Cockatoos
- Zebra Finch
- Rock Ptarmigan
14 Examples of Herbivorous Reptiles
- Desert Tortoise
- Sahara Spiny-Tailed Lizard
- Sinaloa Scrub
- Solomon Island Skink
- Argentina Tortoise
- Chuckwalla
- Desert Iguana
- Uromastyx
- Yellow-Footed Tortoise
- Dryland Tortoise
- Green Iguana
- Mediterranean Tortoise
- Morrocoy
- Prehensile-tailed skinks
7 Examples of Herbivorous Insects
- Butterflies
- Gall wasps
- Moths
- Leaf-mining flies
- Plant bugs
- Weevils
- Leaf beetles
Examples of Herbivorous Invertebrates
- Snails
- Millipedes
- Worms
- Insects
- Slugs
- Mites
Well-known herbivorous animals
- Mula
- Bongo
- Camel
- Deer
- Bumblebee
- Iguana
- Gorilla
- Moth
- Grasshopper
- Antelopes
- Manatee
- Kakapo
- Butterfly
- Honey bee
- Koala
- Hare
- Okapi
- Giraffe
- Ascidias
- Impale
- Bison
- Dugongo
- Capybara
- Kangaroo
- Fruit Bats
- Giant Panda Bear
- Cow
- Goat
- Elephant
- Bushbuck
- Rabbit
- Butter
- Horse
- chinchilla
- Howler Monkey
- Buffalo
- Call
- Hippopotamus
- Beaver
- Caterpillar
Facts and Characteristics of Herbivorous Animals
- Entomologists frequently refer to any of these dietary strategies using the noun “phytophagy” and the adjective “phytophagous.”
- Herbivores are animals that consume plant tissues or plant-based products.
- Herbivory has had both positive and negative impacts on plants over evolutionary time.
- The ability of flowering plants (the Angiosperms) to draw in insect herbivores and use them as pollinators have undoubtedly been advantageous.
- However, some insects can also act as carriers of plant diseases.
- Animals have had to adjust to many of the traits that plants have in order to use them as a food source.
- To defend themselves against toxic substances found in plants, herbivores must have developed detoxification pathways.
- Animal herbivores have the ability to, directly and indirectly, change the composition of plant communities.
- Some herbivores strengthen the defenses of plants.
- Certain plants can exhibit symbiotic interactions with ants that shield their host plants from other herbivores and also regulate the growth of nearby plants through weeding and pruning.
- Plants have a variety of external structures, including leaves, stems, flower components, roots, fruits, and seeds.
- Various plant species may have different versions of each of these structures. Therefore, herbivores should have some traits that enable them to exploit these structures.
- These include hard limbs for digging, saw-like, piercing, or cutting organs (like the chewing mouthparts of insects), and appendages (like claws, spines, or suckers) that allow them to cling to vertical or upside-down surfaces. They should also have wings to reach the tops of the tallest plants.
- The majority and widest variety of herbivores are insects. According to estimates, herbivores make up about half of all living insects.
- To eat hard plant material, herbivorous animals use a variety of strategies.
- These include forming partnerships with other organisms and avoiding hard plant material by consuming plant fluids.
- Other strategies include using chewing mouthparts to gnaw on tough parts and eating soft internal tissue.
References
- Katja Poveda,Ingolf Steffan-Dewenter,Stefan Scheu,Teja Tscharntke (2005). Wiley Online Library (doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.13664.x)
- M. Bonkowski & S. Scheu, 2008. Biotic Interactions in the Rhizosphere: Effects on Plant Growth and Herbivore Development. Ecological Studies, vol 173. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. (doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74004-9_4)
- Australian flora and vegetation statistics, Australian National Botanic Gardens. Available online at (http://www.anbg.gov.au/anbg/australian-flora-statistics.html).