Mitotic cell division definition
The mitotic cell division is an ordered sequence of events by which the nucleus of the cell duplicates and eventually the cell divides into two daughter cells. The cells of multicellular organisms undergo mitotic cell division for organism’s growth and repair or replacement of damaged cells. Mitotic cell division generates two identical daughter cells in which the complete set of chromosomes is found.
Mitotic cell division diagram
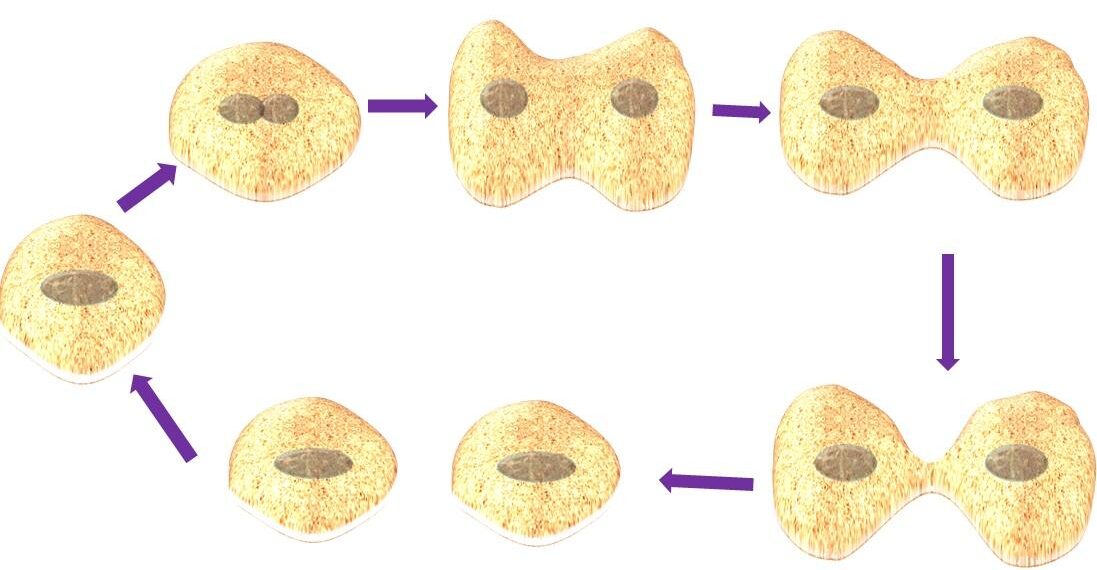
Mitotic cell division process
The cell cycle has two phases 1) Interphase and 2) Mitotic phase.
The interphase is also called as resting phase. Though it is resting phase, it is the main phase during which the cell grows (G1), duplicates its DNA (S), and prepares for mitosis (G2) for later cell division by undergoing cell growth and DNA replication. The mitosis phase is a period during which the actual mitosis (cell division) takes place.
1. The interphase is further divided into three phases such as G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
2. The mitotic phase is further divided into five phases including prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.