Q. Where is DNA located in a prokaryotic cell?
1. Nucleus
2. Nucleolus
3. Nucleoid
4. Mitochondria
Answer: 3 (Nucleoid).
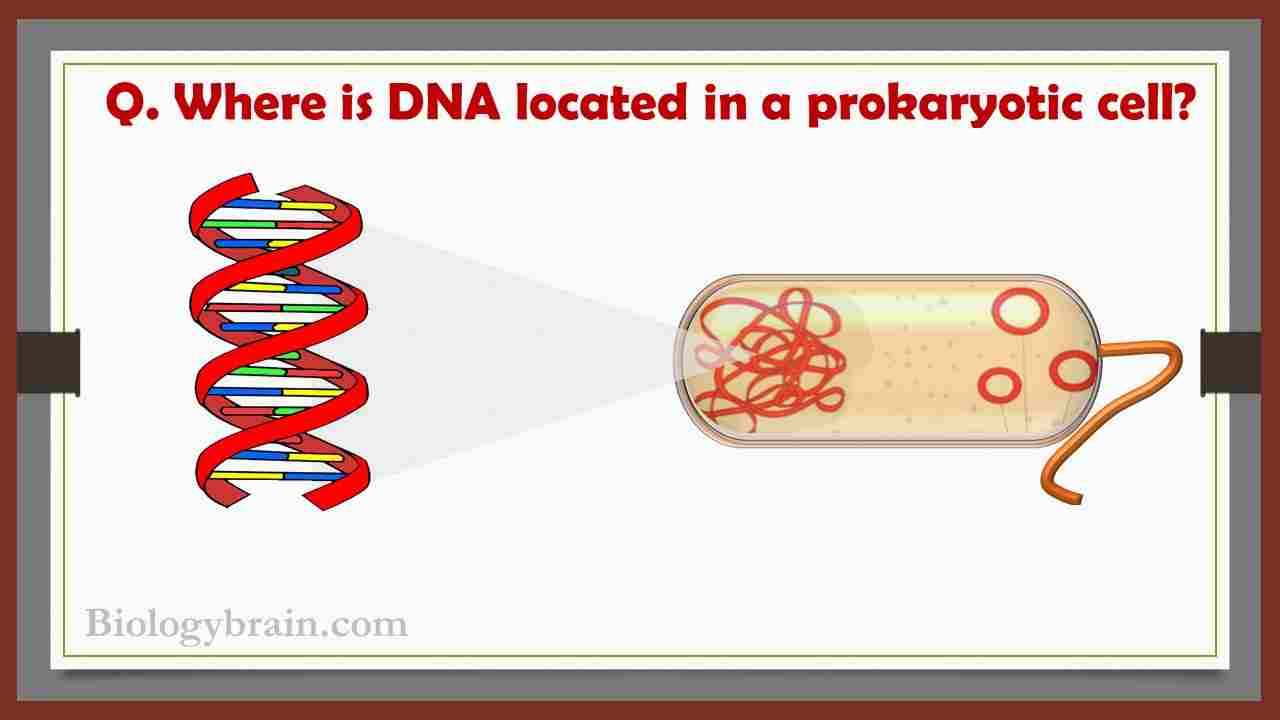
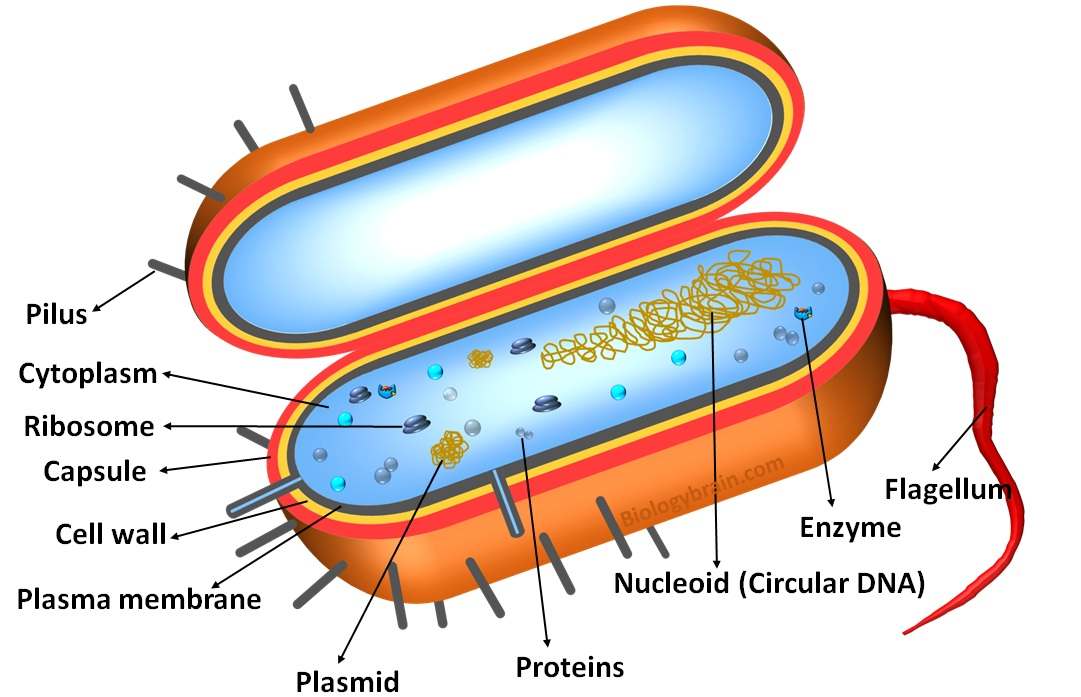
Explanation: Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus, nucleolus, and mitochondria which are cellular compartments in the eukaryotic cells that contain genetic material (DNA). The DNA in prokaryotes is located in a central region of the cell called the nucleoid.
As a nucleus, the nucleoid is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. In addition to nucleoid, there is another independent DNA molecule in the prokaryotes are called a plasmid, which is completely different from the chromosomal DNA of prokaryotes. However, plasmids provide genetic advantages to the prokaryotes in specific conditions.
Example: Multi-drug resistance.
Important questions:
- The alpha-helix and beta-sheet are found at which level of protein organization?
- Which cytoskeletal proteins provide the structural support for microvilli?
- Which of these does not contain a structural protein?
- What level of protein structure is associated with the sequence of amino acids?
- Which of the following pertains to typhoid fever?
- Which of the following tests is an agglutination test for the bacterium causing typhoid fever?
- Questions on nucleic acids
- This is a compound made from a group of covalently bonded atoms?
- If two covalently bonded atoms are identical the bond is?
- Which of the following are characteristics of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR)?
- What are the second messengers in the GPCR-phospholipase c signal transduction system?
- Which of the following have a significant influence on a material’s electrical resistivity?
- What are alleles? And an example.
- What is one difference between the DNA replication of bacteria and eukaryotes?
- Which of the following genotypes is homozygous recessive?
- If q = .4, what is the frequency of homozygous recessive individuals?
- A person who is homozygous recessive at a locus has which of the following?
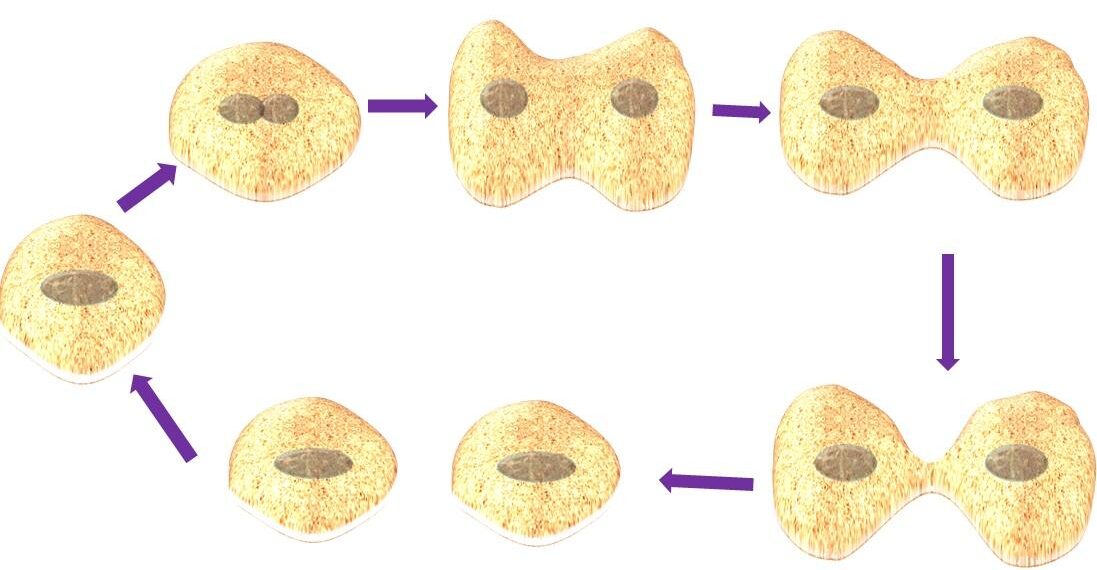
- If cohesin was not produced or not functional what would be the effect on mitosis?
- Which of these is a reverse transcriptase?
- Which of the following functions as cell identity markers, receptors, and enzymes?
- Which cytoskeletal proteins provide the structural support for microvilli?
- The alpha-helix and beta-sheet are found at which level of protein organization?
- Thermogenin in the inner membrane of brown fat cell mitochondria does all of the following except?
- What is ATP synthase and what does it do?
- Brown fat cells produce a protein called Thermogenin
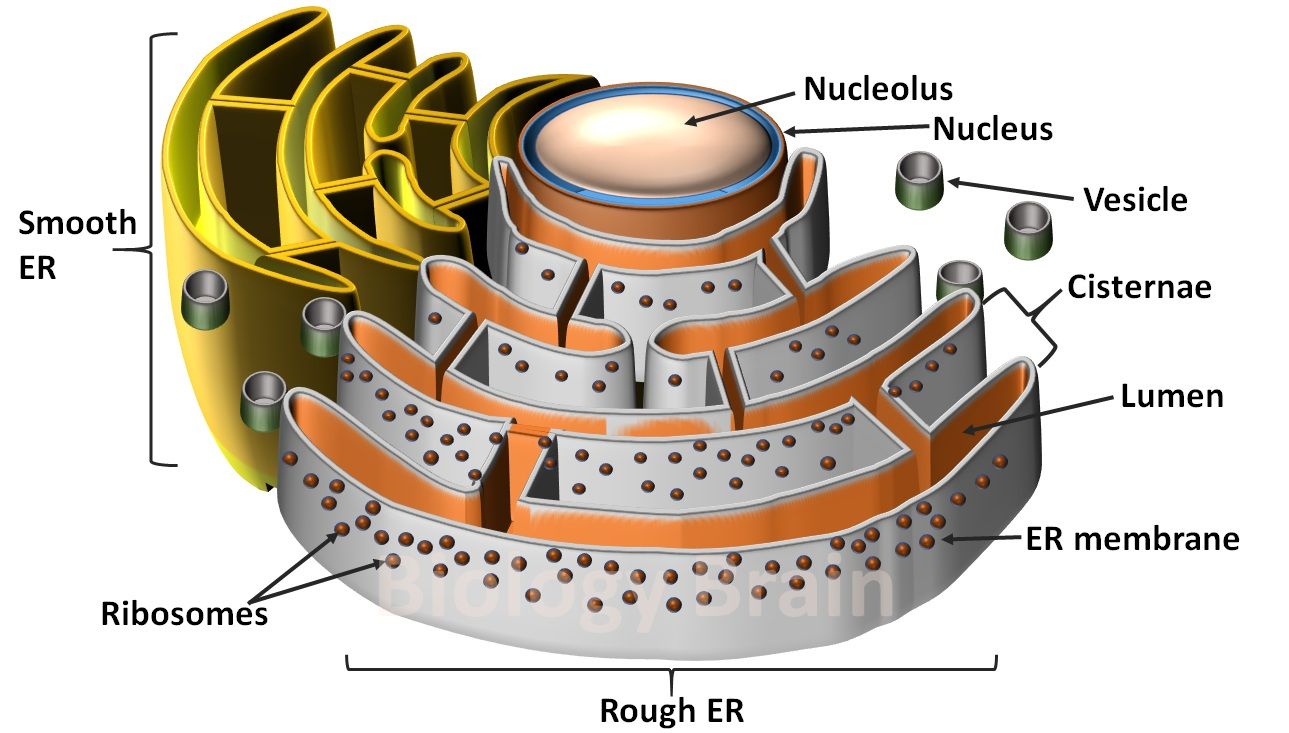
- Which of the following eukaryotic cell structures plays a role in protein trafficking and sorting?
- Which of these does not contain a structural protein?
- After which checkpoint is the cell first committed to continuing the cell cycle through M?
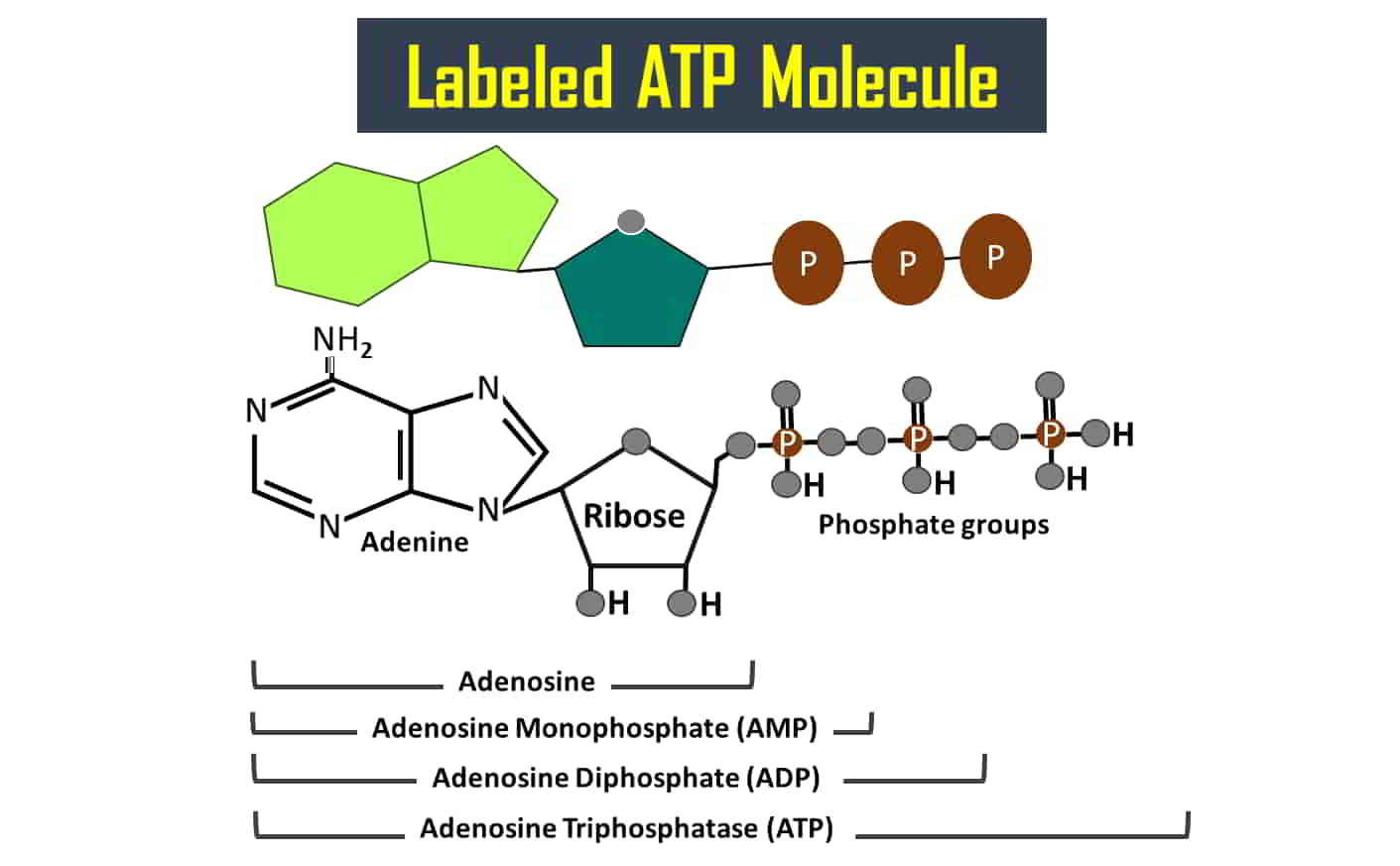
- Which of the following statements about ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is correct?
- What happens in the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
- In general, enzymes are what kinds of molecules?
- The junction between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of the next is called
- What is the role of enzymes in the DNA replication process?
- How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
- In the liver, detoxifying enzymes are localized in what organelle?