Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS)-Definition, Diagram, Function, Structure
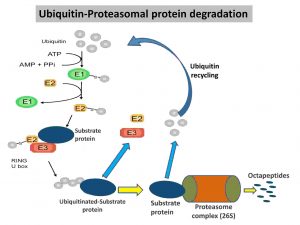
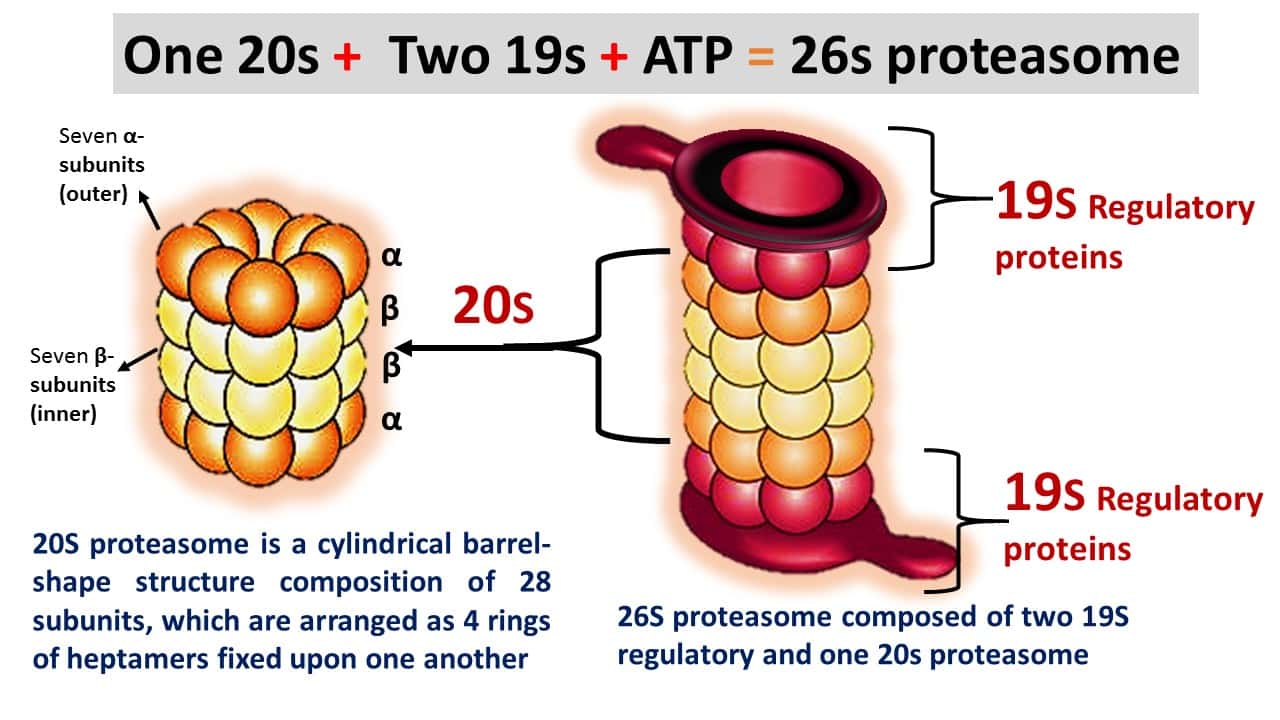
Ubiquitination definition Ubiquitination is a post-translational modification process that plays a major role in protein degradation. The ubiquitin-proteasome system is involved in the process called ubiquitination, ubiquitylation, or molecular “kiss … Read more